¶ MTConnect Agent Pipeline Architecture
¶ Overview
The MTConnect Agent uses a data transformation pipeline to provide a flexible and mutable mechanism for processing incoming data from various sources and allowing for reusability of common transform components.
¶ Transforms
The transfrom is a simple class that takes checks to see if it can transform an entity and, if applicable, applies a transformation to the entity. The result is another entity,
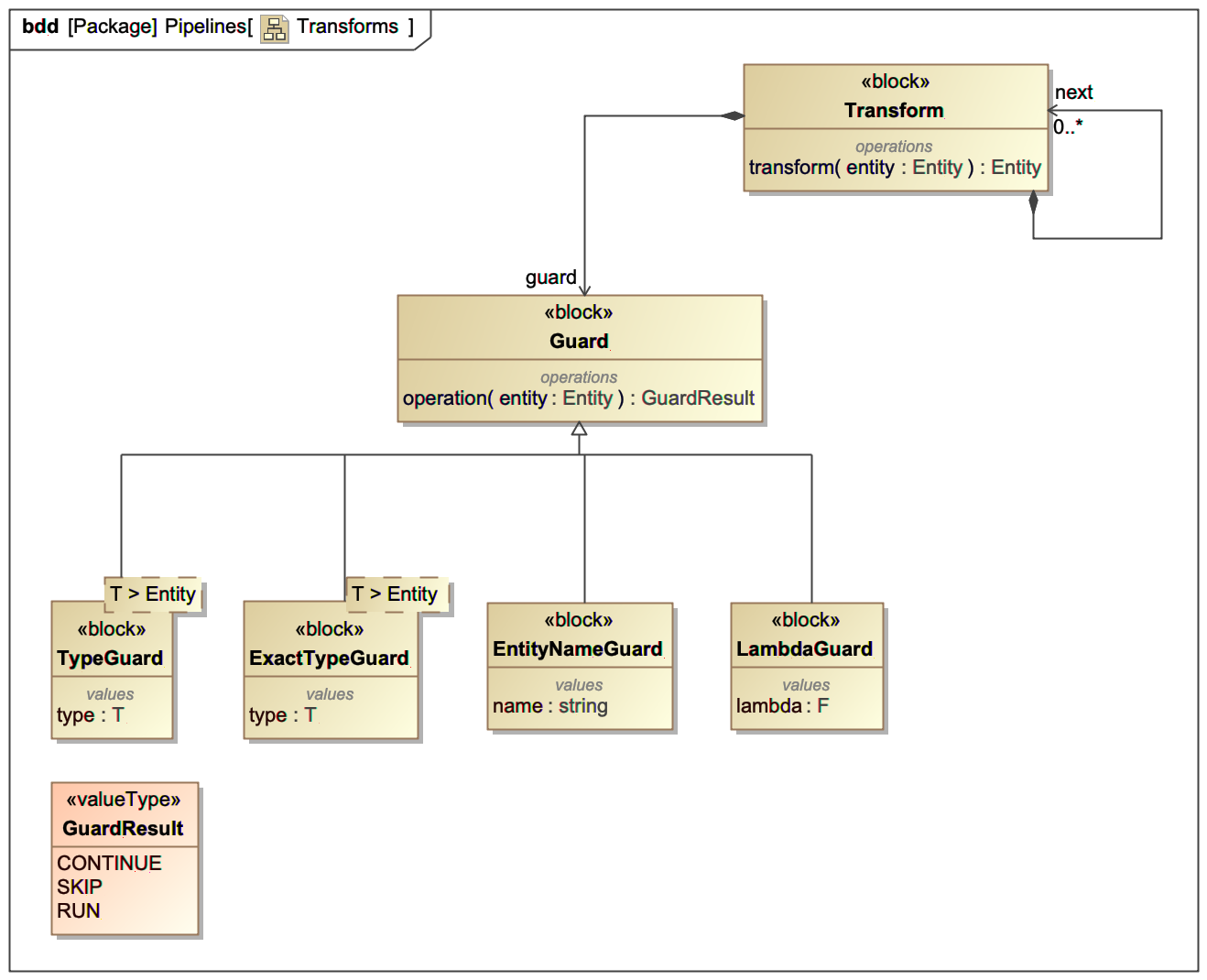
A transform has two required capabilities: Guard and Transform. The Guard allows the transformation to decide if the data is something it can handle if what action should be taken next.
The transform has a list of downstream transforms, each of which is evaluated sequentually. The action is taken based on the result of the Guard. The Guard is a function that matches based on the type of the entity or some other characteristics like the name.
The guard can return one of the three following responses:
CONTINUE: the search for a match will continue to the next transform in the list.SKIP: The search stops, but the transform is not run. The transform's list of next transforms is evaluated to determine the next step.RUN: The transform is executed.
Use the bind method to add a transform, given as an argument to the bind method, to the end of the list of next transforms.
¶ Pipelines
A pipeline is references has a start transform and a build method to construct it. All data source must have a pipeline to deliver data to the agent, sometimes the pipeline is simple, just a delivery transform, as with the loopback pipeline.
Pipelines are also capable of mutating themselves when plugins or scripts are loaded. There are many methods to modify the pipeline.
spliceBefore(const std::string target, TransformPtr transform): Adds this transform directly before thetargettransform. Will replace all references in the lists of next transforms.- ruby:
splice_before(target, transform)
- ruby:
spliceAfter(const std::string target, TransformPtr transform): Adds this transform immediately after thetargettransform. Will replace all references in the lists of next transforms.- ruby:
splice_after(target, transform)
- ruby:
replace(const std::string target, TransformPtr transform): replaces thetargettransform.- ruby:
replace(target, transform)
- ruby:
firstAfter((const std::string target, TransformPtr transform): Inserts the transform at the beginning of the next list oftargettransform's.- ruby:
first_after(target, transform)
- ruby:
lastAfter((const std::string target, TransformPtr transform): Inserts the transform at the end of the next list oftargettransform's.- ruby:
last_after(target, transform)
- ruby:
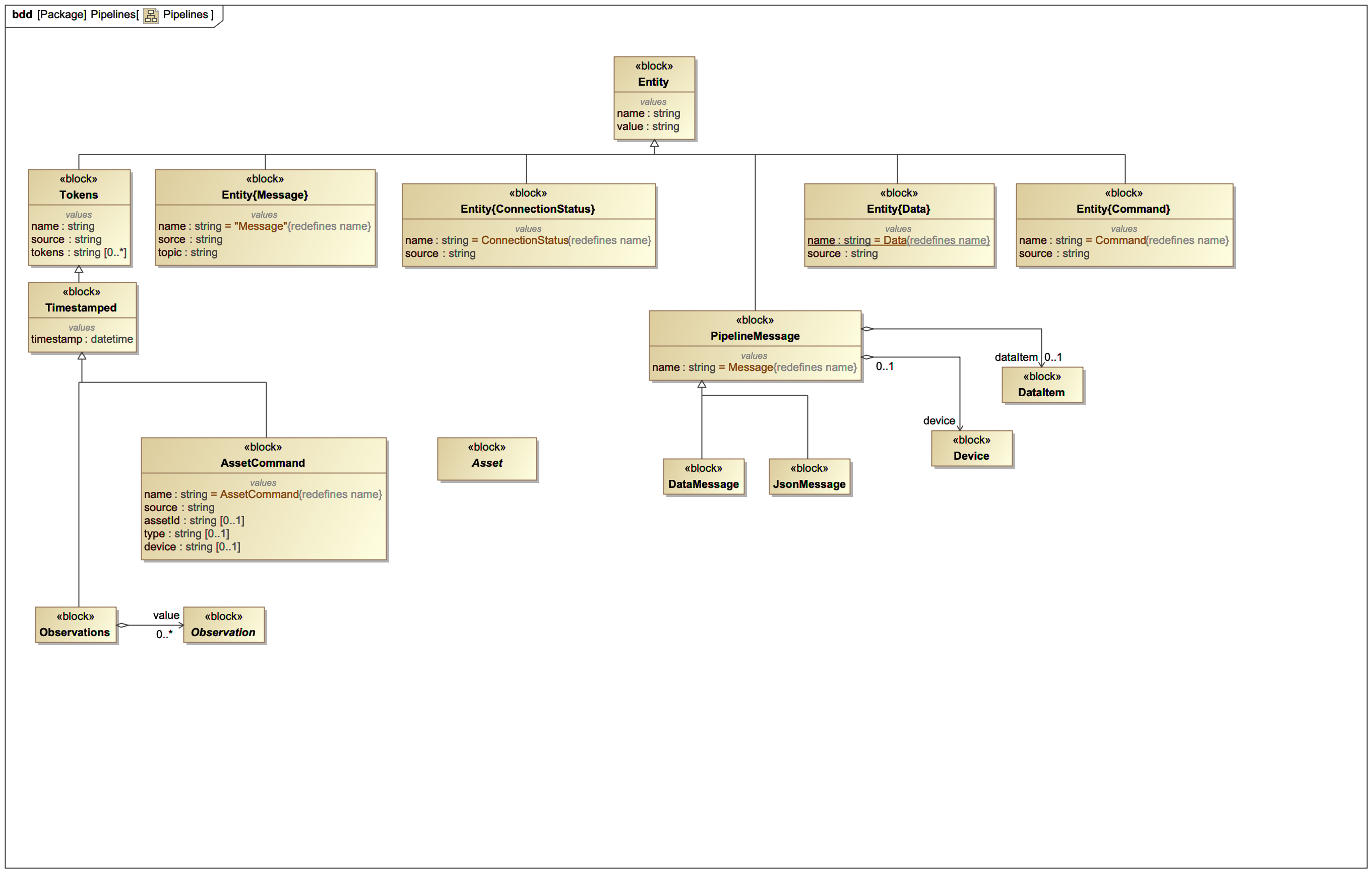
¶ Entities used in the pipelines
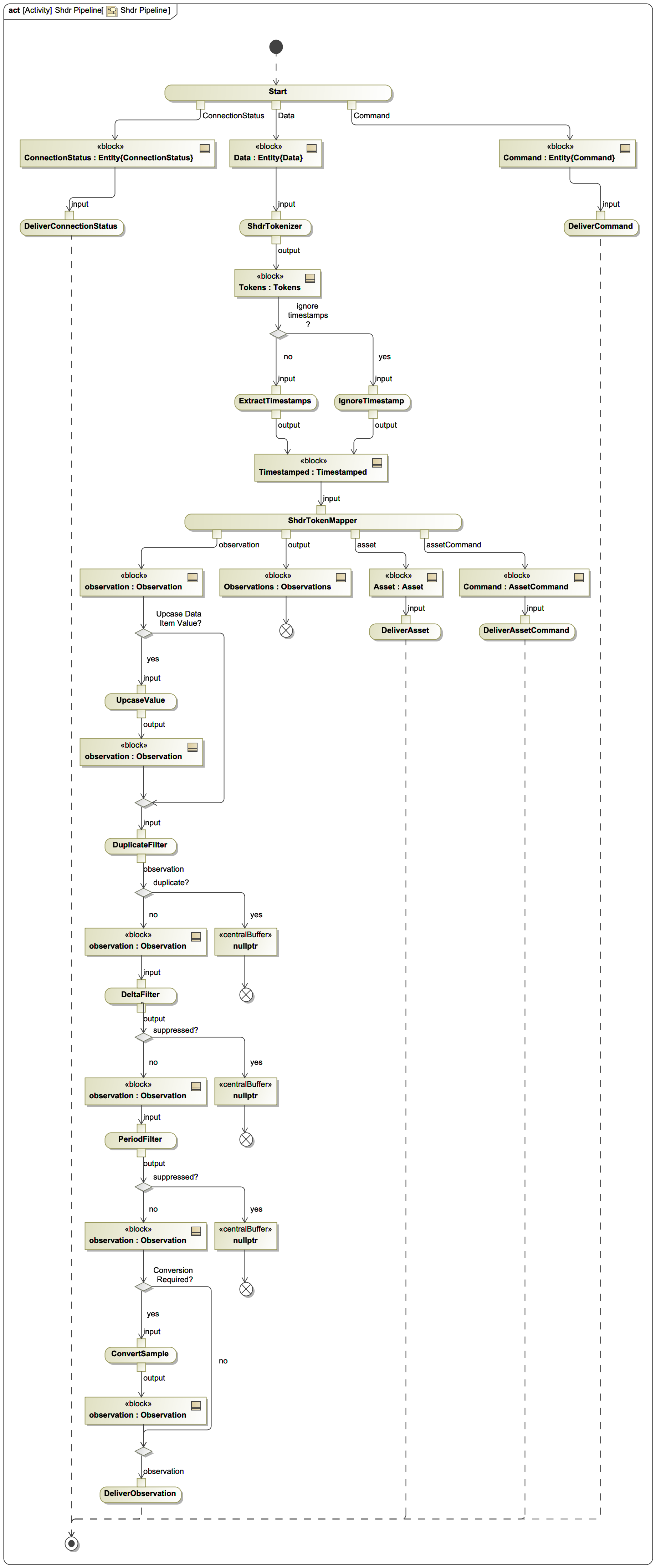
¶ SHDR Adapter Pipeline
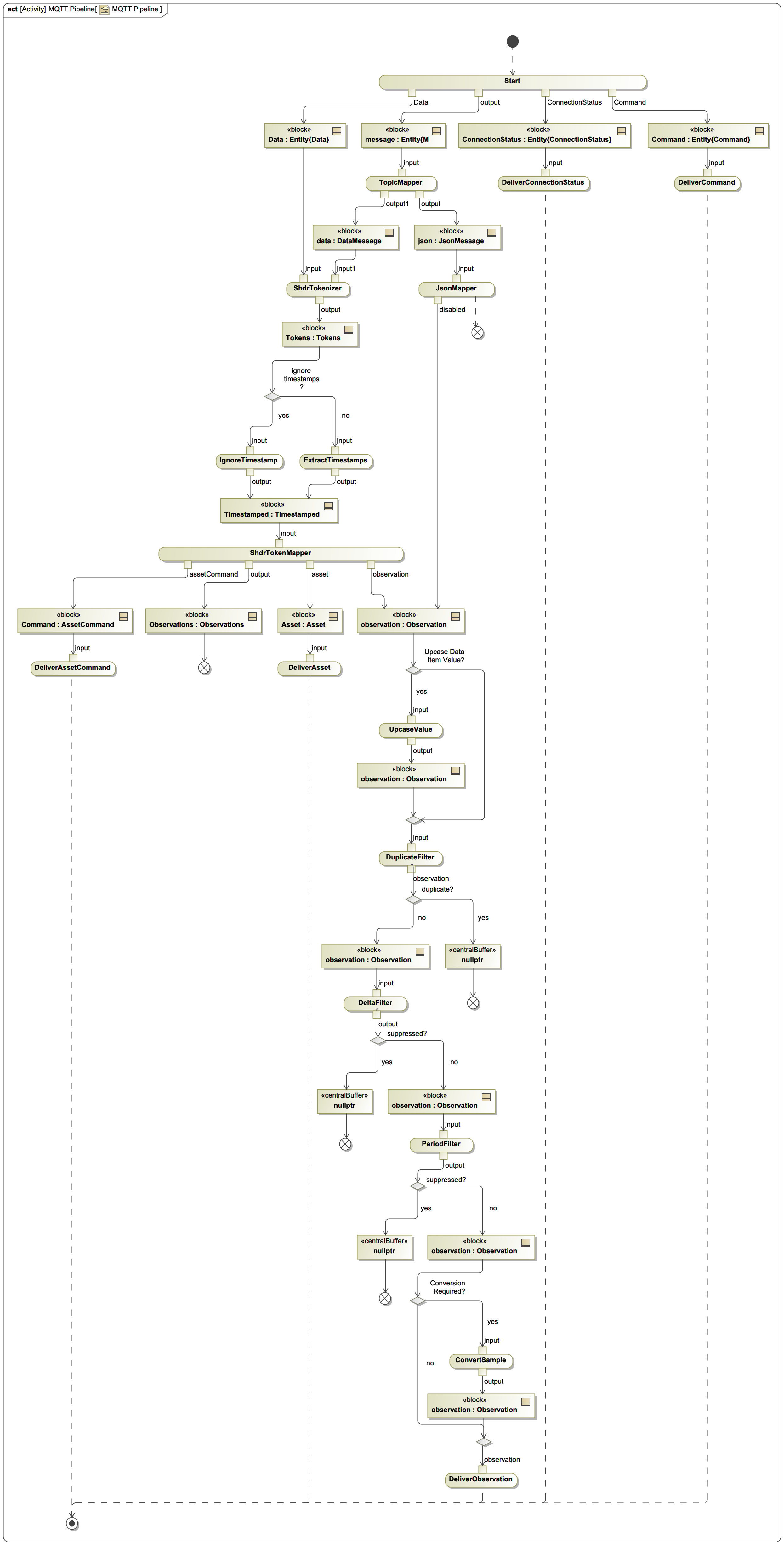
¶ MQTT Adapter Pipeline
Based on the incoming message and topic, the agent attempts to map the topic to a device and data item. Following the attempt to determine the device and data item, it will look at the first character. If it is a { it will create a JsonMessage and forward it to the JsonMapper.
At present the JsonMapper cannot decode the data, so it ignores it. It is assumed this transform will be replaced with a transform that know the specifc json object information model.
If it is data, the payload is assumed to be SHDR and is passed to the SHDR mapper.
¶ Ruby Transforms
When using the mruby embedded language, one can write dynamic scripted transformation. Learn more about how to do so at Data Transformation using Ruby.